Description
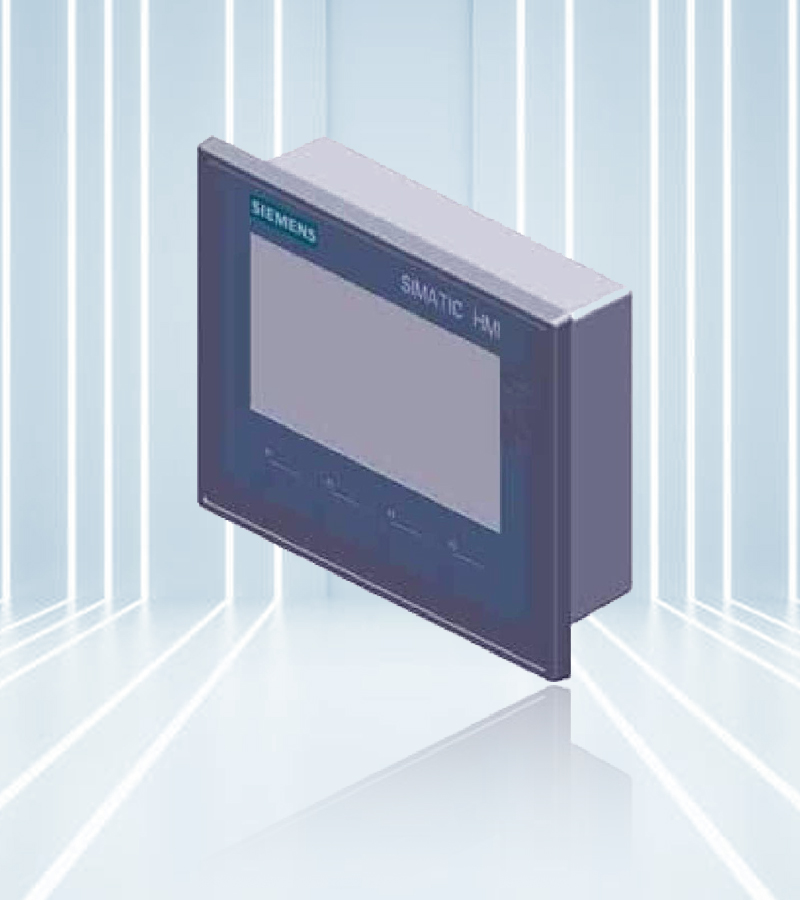
Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) are interactive touch-screen devices that allow operators to monitor and control industrial processes, machinery, and equipment in real-time. These interfaces serve as the bridge between humans and machines, providing intuitive visualizations of system status, performance metrics, and diagnostic information. HMIs offer a range of features and capabilities to streamline industrial control processes. They provide a user-friendly interface with intuitive touch-screen controls, customizable graphics, and menu navigation, allowing operators to easily access and interact with system data and controls.
One of the key advantages of HMIs is their ability to consolidate information from multiple sources into a single interface, providing a comprehensive view of the entire system. Operators can monitor process variables, alarm conditions, and production metrics in real-time, enabling timely decision-making and proactive intervention. HMIs also offer advanced functionality such as data logging, trending, and remote access, allowing operators to track historical performance, analyze trends, and diagnose issues for process optimization and troubleshooting.
With their rugged construction and industrial-grade components, HMIs are designed to withstand harsh environments and demanding operating conditions. They feature sealed enclosures, high-resolution displays, and resistance to dust, moisture, and temperature extremes, ensuring reliable operation in industrial settings. HMIs find applications across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and utilities. They are used in factory automation, process control, machine monitoring, building management systems, and more, providing operators with the tools they need to optimize production, improve efficiency, and ensure the quality of products and processes.
Benefits
- Enhanced Operator Efficiency: HMIs streamline operator interactions with machinery and processes, reducing manual intervention and enabling faster decision-making, leading to improved productivity and efficiency.
- Real-Time Monitoring: HMIs provide real-time visualization of process variables, equipment status, and production metrics, empowering operators to monitor operations closely and respond promptly to changes or issues.
- Remote Accessibility: With remote access capabilities, HMIs allow operators to monitor and control processes from anywhere via network connections, facilitating remote troubleshooting, maintenance, and supervision.
- Customization and Flexibility: HMIs offer customizable interfaces and configurations to suit specific application requirements, enabling adaptation to different processes, workflows, and user preferences.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: HMIs support data logging, trending, and reporting functionalities, enabling operators to analyze historical data, identify trends, and generate reports for performance analysis and regulatory compliance.
Technology
- Touch-Screen Interface: HMIs feature touch-screen displays that allow operators to interact with the system through intuitive gestures, such as tapping, swiping, and pinching, enhancing usability and user experience.
- Embedded Software: HMIs run on embedded software platforms that provide advanced functionality for process visualization, control logic, data management, and communication with other industrial devices and systems.
- Communication Protocols: HMIs support various communication protocols, including Ethernet/IP, Modbus TCP/IP, Profibus, and OPC UA, enabling seamless integration with PLCs, SCADA systems, and other industrial equipment.
- High-Performance Hardware: HMIs are equipped with high-performance hardware components, including processors, memory, and storage, to ensure fast and responsive operation, even in demanding industrial environments.
- Security Features: HMIs incorporate security features such as user authentication, data encryption, and firewall protection to safeguard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats.
Reliability
- Industrial-Grade Construction: HMIs are built with ruggedized enclosures and components that withstand harsh industrial conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity, vibration, and dust ingress.
- Durability: HMIs undergo rigorous testing for reliability and durability, ensuring long-term operation without performance degradation or component failure in industrial environments.
- Fault Tolerance: HMIs incorporate fault-tolerant design features, such as redundant power supplies and storage, to minimize the risk of system downtime and data loss due to hardware failures.
- Continuous Operation: HMIs support hot-swappable components and redundant configurations, enabling uninterrupted operation during maintenance or component replacement activities.
- Lifecycle Support: HMIs are backed by comprehensive lifecycle support, including software updates, technical support, and spare parts availability, ensuring continued functionality and compatibility over the product lifespan.